Have you ever wondered why your dog acts the way it does? Understanding dog behavioral adaptations can unlock the secrets behind your furry friend’s habits and reactions.
These natural changes help dogs survive, communicate, and bond with you. By learning how your dog’s behavior has evolved, you can strengthen your connection and make life easier for both of you. Keep reading to discover fascinating insights that will change the way you see your dog forever.

Credit: bioengineer.org
Innate Canine Behaviors
Dogs have natural behaviors that come from their wild ancestors. These behaviors help them survive and live in social groups. Understanding these instincts helps us care for dogs better.
Some behaviors are linked to hunting, marking territory, and living in packs. These actions show how dogs communicate and protect themselves.
Hunting And Foraging Instincts
Dogs have strong hunting instincts inherited from wolves. They often chase moving objects and use their senses to find food. Even pet dogs may show these behaviors during play.
- Chasing small animals or toys
- Using smell to track scents
- Stalking quietly before pouncing
- Digging to find hidden food
Territorial Marking
Dogs mark their area to keep other animals away. This behavior helps them feel safe and protect their home. They use scent from glands or urine to mark places.
| Marking Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Urine Marking | Leaving scent by urinating on objects |
| Scratch Marking | Scratching the ground to release scent glands |
| Facial Rubbing | Rubbing face on objects to leave scent |
Pack Dynamics
Dogs live in groups called packs. They follow a social order to keep peace. Each dog has a role, like leader or follower. This order helps them work together and stay safe.
- Alpha: The leader who guides the pack
- Beta: The helper who supports the leader
- Omega: The lowest rank, often the peacemaker
- Subordinates: Members who follow the higher ranks

Credit: www.dwdogtraining.com
Communication Methods
Dogs have unique ways to communicate with each other and humans. Their methods are fascinating and diverse.
Understanding these methods helps us connect better with our furry friends.
Body Language Signals
Dogs use body language to express their emotions. They are excellent at communicating through movements and positions.
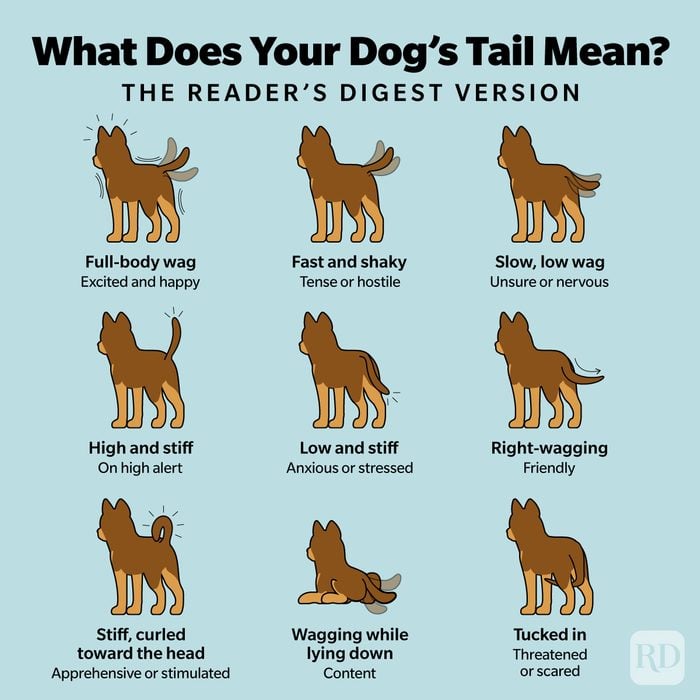
- A wagging tail often means happiness.
- Flattened ears can show fear or submission.
- Raised hackles might indicate aggression or alertness.
- Rolling over can be a sign of trust.
Vocalizations And Their Meanings
Dogs vocalize to express feelings and share messages. Each sound has a distinct purpose.
| Vocalization | Meaning |
| Barking | Attention or alert |
| Whining | Distress or desire |
| Growling | Warning or fear |
| Howling | Communication with others |
Scent Communication
Scent is a powerful tool for dogs. They use it to identify themselves and others.
Dogs leave their scent on objects to mark territory. This helps them communicate with other dogs in the area.
Adaptations To Environment
Dogs change their behavior to live well in different places. They adapt to cities, forests, and homes.
These changes help dogs find food, stay safe, and get along with others.
Behavioral Changes In Urban Settings
Dogs in cities learn to avoid cars and loud noises. They become more alert and careful.
They also change how they find food, often eating scraps or human leftovers.
- Stay close to human areas for food
- Use quiet times to move around safely
- Learn to ignore busy streets and traffic
Survival Strategies In The Wild
Wild dogs use hunting and teamwork to catch prey. They hunt in groups to improve success.
They mark territory with scents to keep other animals away.
- Hunt in packs for larger prey
- Use howling to communicate and call group members
- Stay hidden during the day to avoid danger
Impact Of Domestication
Domestication made dogs more friendly and less fearful of people. They learned to live with humans.
Some natural behaviors changed, but dogs kept skills like guarding and hunting.
- Learn to follow human commands
- Depend on humans for food and care
- Show less aggression towards people
Learning And Socialization
Dogs develop behaviors through learning and social interaction. Their early experiences shape how they act around people and other animals. Understanding these processes helps owners guide their dogs well.
Training and socialization improve a dog’s ability to adapt to new situations. This leads to a happier and safer life for both the dog and its family.
Critical Periods For Behavior Development
Puppies go through special times when they learn best. These periods are key for their social and emotional growth. Missing these times can cause problems later.
- Neonatal period (0-2 weeks): Puppies learn mostly through touch and smell.
- Transitional period (2-4 weeks): They start to open eyes and ears and respond to sounds.
- Socialization period (3-14 weeks): This is when puppies meet new people and animals.
- Juvenile period (3-6 months): Learning becomes more complex and training can be more focused.
Role Of Social Interaction
Dogs need to meet other dogs and people to build good social skills. Positive interactions help them feel safe and reduce fear or aggression. Social play teaches dogs how to behave politely.
| Type of Interaction | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Playing with other dogs | Learn bite control and body language |
| Meeting new people | Become friendly and less fearful |
| Exposure to different environments | Adapt to new sights and sounds |
| Training sessions | Strengthen owner-dog bond |
Training And Behavioral Modification
Training helps dogs learn good habits and stop bad ones. Consistent commands and rewards work best. Behavioral changes happen faster with patience and clear signals.
- Use short training sessions often.
- Give treats or praise for good behavior.
- Avoid punishment to prevent fear.
- Practice commands in different places.
- Be patient and keep routines steady.
Stress And Coping Mechanisms
Dogs can feel stress just like people. They show it in different ways. Understanding their stress helps us care better for them.
Dogs use many ways to handle stress. These ways are called coping mechanisms. They help dogs stay calm and safe.
Signs Of Anxiety In Dogs
Dogs show anxiety through their actions and body language. Watching closely can help spot stress early.
Common signs include changes in behavior and physical symptoms. These signs tell us the dog needs comfort.
- Restlessness or pacing
- Excessive barking or whining
- Shaking or trembling
- Hiding or trying to escape
- Yawning or licking lips often
- Changes in appetite
- Destructive chewing or digging
Common Stress Triggers
Dogs feel stress from many sources. Knowing these triggers helps prevent anxiety.
Some triggers are loud noises, new places, or separation from owners. Other triggers come from health problems.
- Loud sounds like fireworks or thunder
- Strangers or unfamiliar animals
- Changes in routine or environment
- Being left alone for long times
- Travel or car rides
- Health issues or pain
Natural Stress Relief Behaviors
Dogs use natural behaviors to calm themselves. These actions help lower stress without help from others.
Some behaviors include chewing, digging, or seeking comfort from people. These actions are important for their well-being.
- Chewing on toys or bones
- Digging in the yard or soil
- Rolling on the ground
- Shaking their body
- Seeking pets and cuddles
- Sniffing and exploring their environment
Evolutionary Roots
Dogs have changed a lot from their wild ancestors. Their behavior shows how they adapted over time.
Studying these changes helps us understand why dogs act the way they do today.
From Wolves To Modern Dogs
Dogs come from wolves that lived thousands of years ago. People started to tame some wolves for help and company.
This long process changed wolves into dogs. They became less wild and more friendly toward humans.
Genetic Influences On Behavior
Genes play a big role in how dogs behave. Different genes affect their instincts and reactions.
- Genes control traits like barking and guarding
- Some genes make dogs more social or calm
- Behavior can be passed from parents to puppies
- Selective breeding changes gene mixes over time
Breed-specific Traits
| Breed | Behavioral Trait | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Border Collie | High intelligence and herding | Manage livestock |
| Beagle | Strong scent tracking | Hunting small game |
| Bulldog | Calm and stubborn | Companion |
| German Shepherd | Loyal and protective | Police and guard work |
Credit: www.rd.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Common Dog Behavioral Adaptations?
Dogs adapt by developing social skills, communication signals, and problem-solving abilities. These behaviors help them survive and thrive with humans and other animals.
How Do Dogs Adapt To Different Environments?
Dogs change their behavior based on climate, living space, and social settings. They may alter activity levels, grooming habits, and interaction patterns to fit their surroundings.
Why Do Dogs Exhibit Protective Behavior?
Protective behavior is an adaptation for guarding territory and family. It helps dogs sense threats early and respond to keep their pack safe.
Can Dog Behavioral Adaptations Improve Training?
Yes, understanding these adaptations helps trainers use effective methods. Tailoring training to a dog’s natural behaviors boosts learning and strengthens bonds.
Conclusion
Dogs change their behavior to live well with humans and nature. These changes help them find food, stay safe, and communicate better. Understanding these behaviors can improve how we care for them every day. Dogs show us how they adapt and survive in many ways.
Watching their actions teaches us patience and kindness. Every dog has unique habits shaped by their past and surroundings. Paying attention to these traits helps build a stronger bond between dogs and people. It’s a simple step toward happier, healthier pets.

Emily Barker is the founder of ChillDogLife.com, a space dedicated to helping pup parents discover the best dog products, lifestyle tips, and cozy ideas for happier homes.
A lifelong dog lover, Emily combines her passion for pets with a knack for research to share trusted recommendations on everything from toys and furniture to health and everyday care.
Her goal is simple: to make life easier, stylish, and more joyful for dogs and the people who love them.







