Have you ever wondered how neutering might change your dog’s behavior? If you’re thinking about neutering your furry friend, understanding what to expect can make a big difference.
You want the best for your dog, and knowing how this procedure affects their actions helps you prepare and care for them better. Keep reading to discover the surprising ways neutering can influence your dog’s behavior—and how you can support your pet through these changes.

Credit: www.fitwarm.com
Behavioral Shifts After Neutering
Neutering a dog can cause changes in its behavior. These changes often help dogs become calmer and more focused. It is important to understand what shifts to expect after neutering.
Different dogs react in various ways, but many show common patterns. These patterns include less aggression, reduced marking, and fewer roaming behaviors.
Reduced Aggression
Neutered dogs tend to have less aggressive behavior. This happens because hormone levels drop, which lowers some types of dominant and defensive actions.
- Less growling and barking at other dogs
- Reduced fighting and biting risks
- Calmer reactions to strangers and loud noises
Decreased Marking Habits
Marking territory with urine is a common behavior in male dogs. Neutering often leads to a drop in this marking habit.
| Before Neutering | After Neutering |
| Frequent marking inside and outside | Much less frequent or no marking |
| Strong scent marking to claim territory | Weaker or no scent marking |
| Marking triggered by new smells or dogs | Lower response to triggers |
Lowered Roaming Tendencies
Many dogs roam to find mates or explore new areas. Neutering reduces the desire to roam far from home.
Common signs of lowered roaming include:
- Staying closer to home
- Less interest in escaping the yard
- Reduced risk of getting lost or injured

Credit: zigly.com
Impact On Social Interactions
Dog neutering can change how dogs interact socially. These changes may affect their play behavior and dominance signals. Understanding these changes helps in managing social interactions better.
Neutering can lead to a calmer demeanor in some dogs. Social dynamics might shift, influencing how dogs relate to each other.
Changes In Play Behavior
Neutered dogs may show changes in how they play. Some dogs become less aggressive and more relaxed during playtime.
Other dogs may play less often or with less energy. These changes can alter group play dynamics with other dogs.
- Reduced roughhousing during play
- Increased interest in gentle games
- Less frequent play invitations
Altered Dominance Signals
Neutering can change how dogs show dominance. Some neutered dogs may not exhibit strong dominance signals.
This can lead to fewer conflicts with other dogs. It’s important to watch how these changes affect the dog’s social rank.
| Dominance Signal | Possible Change |
| Mounting | Decreased frequency |
| Growling | Less intense |
| Body Posture | More neutral stance |
Training Adjustments Post-neutering
Neutering can change a dog's behavior and training needs. Owners should adjust training methods after the procedure.
Understanding these changes helps keep training effective and supports the dog’s well-being.
Improved Focus And Obedience
Neutered dogs often show better attention during training. They may respond faster to commands and stay focused longer.
- Use shorter, more frequent training sessions to maintain interest.
- Reward calm and attentive behavior to reinforce focus.
- Increase distractions slowly as the dog improves.
Managing Energy Levels
Neutering can lower a dog’s energy. Training should match this change to avoid frustration or boredom.
| Energy Level | Training Tip |
| High | Include more physical activities like fetch or running. |
| Moderate | Balance exercise with mental games and obedience training. |
| Low | Focus on gentle training and short play sessions. |
Health-related Behavior Changes
Neutering affects a dog’s behavior beyond reproduction. It can lead to changes in health and habits. Understanding these shifts helps owners care better for their pets.
Two common changes after neutering are weight management challenges and shifts in activity preferences. Both can impact a dog’s overall well-being.
Weight Management Challenges
Neutered dogs may gain weight more easily. Their metabolism often slows down, and they may feel less hungry or more relaxed.
- Metabolism slows, burning fewer calories
- Appetite may increase or stay the same
- Lower activity can reduce calorie use
- Weight gain can lead to health issues like joint pain
- Watch food portions carefully
Shifts In Activity Preferences
After neutering, dogs may change how they like to spend their energy. Some become calmer, while others keep their usual energy levels.
| Activity Type | Typical Change | Owner Tips |
| Running and Playing | May decrease in some dogs | Encourage short play sessions daily |
| Walking | Often remains steady | Keep regular walking routines |
| Resting | Usually increases | Provide comfortable resting areas |
Myths Versus Facts About Neutering
Many people have questions about neutering dogs. Some ideas are true, but others are not. It is important to know the facts before making a choice.
This article looks at common myths and what science says about neutering. Understanding this helps you care for your dog better.
Common Misconceptions
Some believe neutering changes a dog’s personality. Others think it causes health problems or makes dogs lazy. These ideas are not always true.
- Myth: Neutering makes dogs aggressive.
- Myth: Dogs gain too much weight after neutering.
- Myth: Neutering is painful and dangerous.
- Myth: Only male dogs should be neutered.
Scientific Insights
Research shows neutering helps reduce some behaviors like roaming and marking. It can also lower risks of certain diseases.
| Myth | Fact |
| Neutering causes aggression | Often reduces aggressive acts |
| Neutering leads to obesity | Weight gain is due to diet, not neutering |
| Neutering is always risky | It is a common, safe procedure |
| Only males need neutering | Females benefit from spaying too |
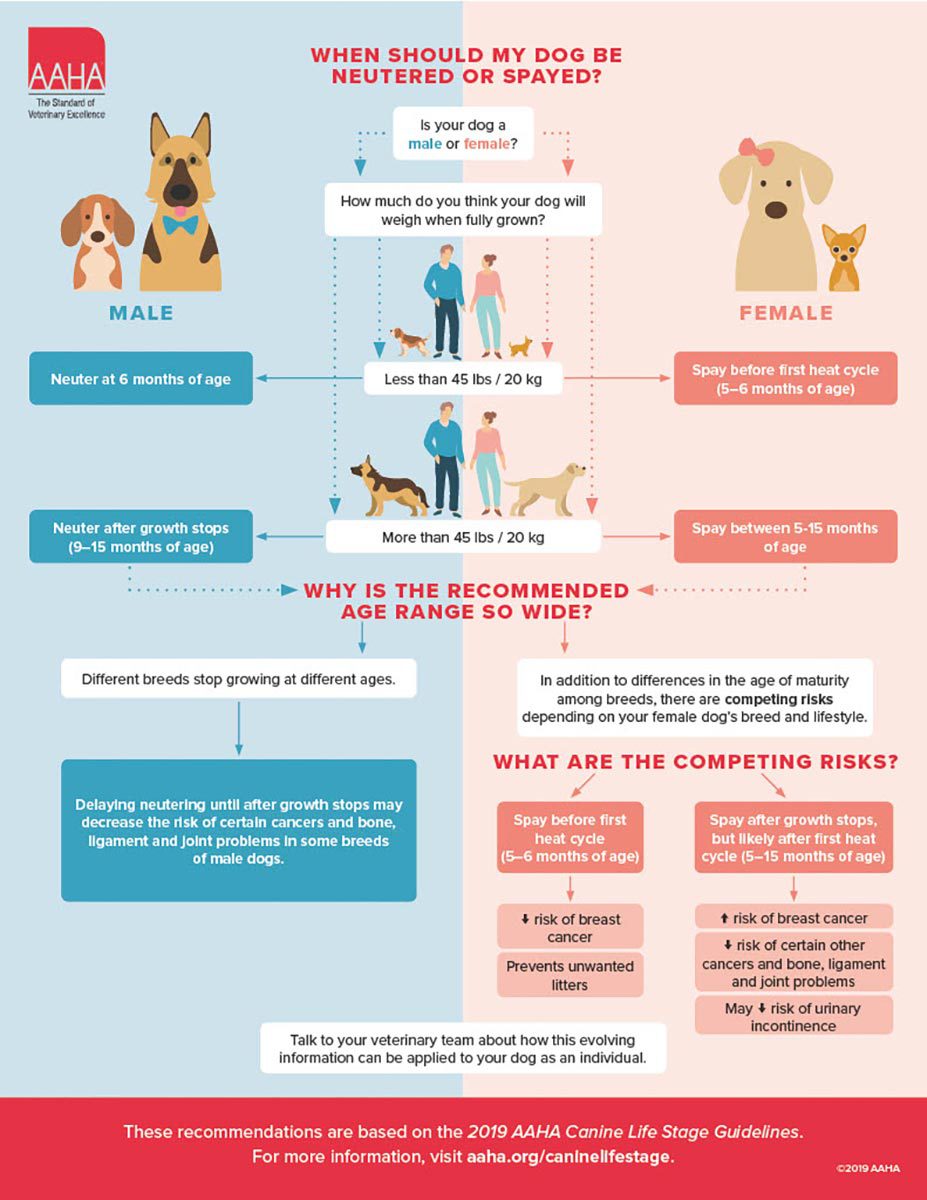
Timing And Its Effects On Behavior
Neutering dogs can affect their behavior in different ways. The timing of neutering plays a big role in these changes. Choosing the right time helps manage behaviors better.
Understanding when to neuter your dog can help reduce unwanted actions like aggression or anxiety. It also supports their healthy growth and social skills.
Early Versus Late Neutering
Neutering early means before six months of age. Late neutering happens after the dog reaches maturity. Each choice affects behavior and health differently.
- Early neutering may lower risks of some cancers.
- Late neutering might reduce joint problems in some breeds.
- Early neutering often lowers aggressive behavior.
- Late neutering can let some natural behaviors develop fully.
- Early neutering may increase fear or anxiety in some dogs.
Breed-specific Considerations
Different dog breeds react differently to neutering times. Large breeds may need to wait longer to neuter. Small breeds often do well with early neutering.
| Breed Size | Recommended Neutering Time | Behavior Effects |
| Small Breeds | Before 6 months | Less marking, lower aggression |
| Medium Breeds | 6-12 months | Balanced growth and behavior |
| Large Breeds | After 12 months | Lower joint issues, natural maturity |
Owner Tips For Supporting Behavior Changes
Neutering can change your dog's behavior. These changes need your support and care. Understanding how to help your dog adjust makes a big difference.
Use simple methods to guide your dog through this time. This helps keep your dog calm and happy.
Positive Reinforcement Techniques
Reward good behavior with treats and praise. This helps your dog learn what you want. Avoid punishing bad behavior because it can cause fear.
- Give a treat when your dog stays calm
- Use a gentle voice to say “good job”
- Play with your dog after good behavior
- Ignore unwanted behavior instead of yelling
- Keep training sessions short and fun
Monitoring And Adjusting Routines
Watch your dog’s daily habits and mood closely. Change routines slowly to avoid stress. Keep feeding, walking, and playtimes steady.
| Routine | Before Neutering | After Neutering | Tips |
| Feeding | Twice a day at set times | Keep same schedule | Use smaller meals if appetite changes |
| Walking | 30 minutes, twice daily | Shorter walks first week | Increase time gradually |
| Playtime | Active games daily | Gentle play first few days | Watch for tired signs |
Credit: southeastoakvillevet.ca
Frequently Asked Questions
What Behavioral Changes Occur After Dog Neutering?
Neutering often reduces aggression and territorial marking. Dogs tend to be calmer and less prone to roaming. However, some behaviors may remain unchanged due to personality or training.
Does Neutering Reduce Dog Aggression?
Yes, neutering can lower hormone-driven aggression. It helps especially in male dogs displaying dominance or territorial behaviors. Yet, training and socialization are also crucial for behavior improvement.
How Soon After Neutering Do Behaviors Change?
Behavioral changes usually begin within weeks after surgery. Full effects may take several months as hormones stabilize. Patience and consistent training support positive outcomes.
Can Neutering Affect A Dog’s Energy Levels?
Neutered dogs often show decreased hyperactivity. Energy becomes more manageable, aiding training and social interactions. Proper exercise remains important to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Conclusion
Neutering can change many dog behaviors for the better. It helps reduce aggression and roaming. Dogs often become calmer and more focused. Neutering also lowers the risk of certain health problems. Remember, it is important to discuss timing with your vet.
Every dog reacts differently after the procedure. Watch your dog closely and give lots of love. This choice supports both your pet’s health and your home’s peace. Taking care of behavior through neutering is a kind step for dogs.

Emily Barker is the founder of ChillDogLife.com, a space dedicated to helping pup parents discover the best dog products, lifestyle tips, and cozy ideas for happier homes.
A lifelong dog lover, Emily combines her passion for pets with a knack for research to share trusted recommendations on everything from toys and furniture to health and everyday care.
Her goal is simple: to make life easier, stylish, and more joyful for dogs and the people who love them.







